Mass Migration: The Growing Tide
The Consequences for Displaced Peoples
The phenomenon of mass migration, defined as the large-scale movement of people from one geographical location to another, has emerged as a defining feature of the 21st century. This growing tide of migration is driven by a complex interplay of factors including conflict, economic disparities, environmental changes, and political instability.
The consequences for displaced peoples are profound, affecting their socio-economic status, mental and physical health, and their integration into new communities. International organizations and governments play pivotal roles in managing these movements and addressing the myriad challenges that arise. Here we look into the key drivers of mass migration, the impact on displaced populations, and the responses from the global community.
*Youtube Video Taken From the Promises Project Film ‘Loved by Ghosts‘
Table of Contents

Conflict and Violence
One of the primary drivers of mass migration is conflict and violence. Wars, civil strife, and persecution force millions to flee their homes in search of safety. For instance, the Syrian civil war, which began in 2011, has displaced over 13 million people, both internally and as refugees in neighbouring countries and beyond. Similarly, ongoing conflicts in Afghanistan, South Sudan, and Yemen have created significant refugee flows. These conflicts often result in severe human rights violations, leaving people with no choice but to abandon their homes to escape imminent danger.
Economic Disparities
Economic disparities also significantly contribute to migration. People from less developed countries often migrate to more developed nations in search of better economic opportunities. This form of migration is driven by the hope for improved living standards, employment, and education. For example, Latin American migrants heading towards the United States are often motivated by the promise of better job prospects and living conditions. In many cases, the countries they leave behind are plagued by high unemployment rates, low wages, and limited economic growth, which perpetuate cycles of poverty and compel people to seek better opportunities abroad.

Environmental Changes
Environmental changes are increasingly recognized as a major driver of migration. Climate change and environmental degradation lead to resource scarcity, food insecurity, and habitat loss, pushing people to migrate. Rising sea levels, extreme weather events, and prolonged droughts disrupt livelihoods, particularly in agriculture-dependent regions. For example, desertification in the Sahel region of Africa has forced many to migrate in search of arable land and water. Similarly, the Pacific Islands face existential threats from rising sea levels, prompting entire communities to relocate.
Political Instability and Governance Issues
Political instability and governance issues also play a crucial role in driving mass migration. Corruption, lack of rule of law, and poor governance create environments where people feel insecure and disenfranchised. Authoritarian regimes and political persecution force individuals to flee to escape oppression. Venezuela, for instance, has seen a mass exodus due to economic collapse and political repression under the Maduro regime. Such political conditions often exacerbate economic difficulties and social unrest, creating a vicious cycle that drives people to migrate.

Socio-Economic Hardships
The consequences for displaced peoples are multifaceted and profound. Displacement often results in significant socio-economic hardships. Refugees and migrants frequently face difficulties in securing employment, housing, and access to basic services in their host countries. These challenges are compounded by legal and social barriers, such as language differences, discrimination, and lack of documentation. For instance, Syrian refugees in Lebanon and Jordan struggle with limited access to formal employment and adequate housing, leading to precarious living conditions and economic instability.
Mental and Physical Health Issues
Mental and physical health issues are also prevalent among displaced populations. The trauma of displacement, loss of home, and the journey itself can have lasting psychological effects. Many refugees experience anxiety, depression, and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). Additionally, access to healthcare is often limited in refugee camps and host communities, exacerbating health problems. For example, Rohingya refugees in Bangladesh face significant health challenges due to overcrowded camps and inadequate healthcare facilities, leading to outbreaks of diseases such as cholera and diphtheria.

Integration Challenges
Integration into new communities poses another significant challenge for displaced peoples. Social cohesion and acceptance by host communities are crucial for successful integration. However, migrants often face xenophobia, discrimination, and social exclusion. These attitudes can hinder their ability to integrate, find employment, and contribute to the local economy. In Europe, for instance, the influx of refugees from the Middle East and Africa has sparked debates and tensions over cultural integration and national identity, sometimes leading to restrictive immigration policies and rising nationalist sentiments.
United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees (UNHCR)
International organizations and governments play vital roles in managing mass migration and addressing its consequences. The United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees (UNHCR) is a key player in providing protection and assistance to refugees and internally displaced persons (IDPs). The UNHCR works to ensure that displaced populations have access to shelter, food, healthcare, and education. It also advocates for durable solutions, such as voluntary repatriation, local integration, or resettlement to third countries. For example, the UNHCR has been instrumental in coordinating the international response to the Syrian refugee crisis, providing critical support to millions of displaced Syrians.

Government Responsibilities
Governments, both in origin and host countries, also have significant responsibilities in managing migration. Countries of origin need to address the root causes of migration, such as conflict, economic instability, and poor governance, through policies that promote peace, development, and good governance. Host countries, on the other hand, must develop comprehensive migration policies that balance humanitarian obligations with national interests. This includes providing asylum, protecting the rights of migrants, and facilitating their integration into society. For instance, Germany’s open-door policy during the 2015 refugee crisis was a significant humanitarian gesture, but it also required substantial efforts to integrate the large number of arrivals into German society and the labour market.
International Cooperation
International cooperation is crucial for effectively managing mass migration. Multilateral frameworks and agreements, such as the Global Compact for Safe, Orderly and Regular Migration and the Global Compact on Refugees, provide guidelines for international cooperation and responsibility-sharing. These agreements emphasize the need for a coordinated global response, respect for human rights, and support for countries hosting large numbers of refugees and migrants. They also stress the importance of addressing the root causes of migration and enhancing legal pathways for migration to reduce the reliance on dangerous and irregular routes.

Role of NGOs and Civil Society
In addition to international organizations and governments, non-governmental organizations (NGOs) and civil society play essential roles in supporting displaced populations. NGOs often provide critical services, such as legal assistance, healthcare, education, and psychosocial support, complementing the efforts of international organizations and governments. For example, Médecins Sans Frontières (Doctors Without Borders) provides medical care in refugee camps and conflict zones, addressing the urgent health needs of displaced populations. Similarly, organizations like Save the Children focus on the protection and education of displaced children, ensuring they have access to safe learning environments and support.
Contribution of the Private Sector
The private sector also has a role to play in addressing the challenges of mass migration. Businesses can contribute by providing employment opportunities for migrants and refugees, investing in communities hosting large numbers of displaced people, and supporting initiatives that promote social cohesion and economic integration. For instance, some companies have launched programs to hire some refugees and support their integration into the workforce, demonstrating the positive impact that the private sector can have on migration issues.
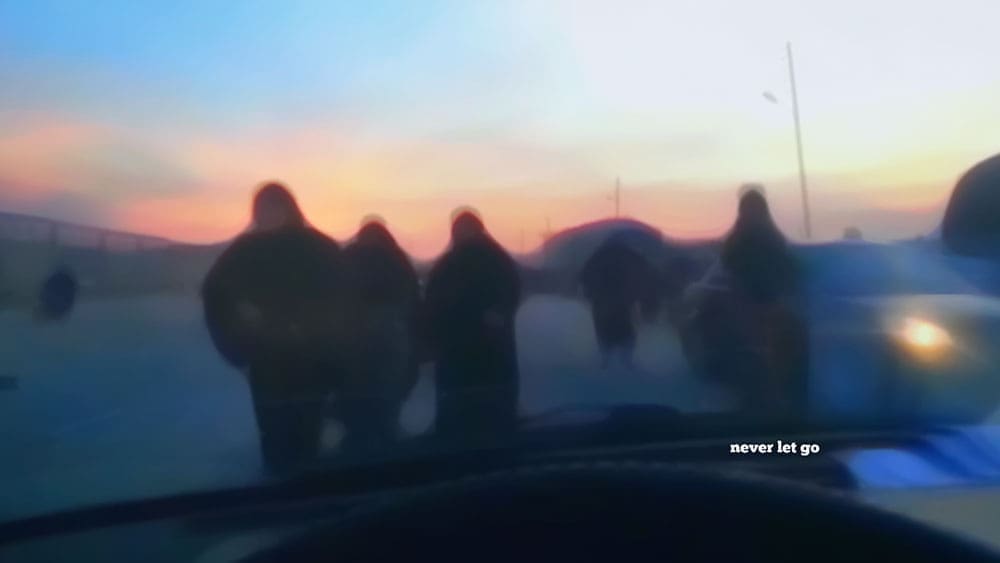

Challenges and Solutions
Despite these efforts, significant challenges remain in addressing the growing tide of mass migration. The scale of displacement often overwhelms the capacity of host countries and international organizations to provide adequate support. Funding shortages, political opposition, and logistical difficulties hamper effective responses. Moreover, the global political climate, characterized by rising nationalism and anti-immigrant sentiments, complicates efforts to develop and implement comprehensive migration policies.
Addressing the challenges of mass migration requires a multifaceted approach that includes preventive measures, immediate assistance, and long-term solutions. Preventive measures involve addressing the root causes of migration, such as conflict, poverty, and environmental degradation, through development aid, conflict resolution, and climate change mitigation. Immediate assistance includes providing humanitarian aid, protection, and basic services to displaced populations, ensuring their safety and dignity. Long-term solutions involve finding durable solutions for displaced peoples, such as voluntary repatriation, local integration, or resettlement to third countries, and promoting their socio-economic integration into host communities.

A Complex Interplay of Factors
The growing tide of mass migration is driven by a complex interplay of factors including conflict, economic disparities, environmental changes, and political instability. The consequences for displaced peoples are profound, affecting their socio-economic status, health, and integration into new communities. International organizations, governments, NGOs, and the private sector play crucial roles in managing migration and addressing its challenges.
However, significant efforts are still needed to develop comprehensive, coordinated, and sustainable responses to ensure the protection and well-being of displaced populations. By addressing the root causes of migration and enhancing international cooperation, the global community can better manage the complexities of mass migration and support those who are forced to leave their homes in search of safety and better opportunities.
























Leave a Comment