The Strength of Revolution
Political Transformation & The Strength of Revolution
Revolution, a concept deeply embedded in human history, is a formidable force that can bring about fundamental and relatively sudden changes in political power and organization. It often emerges when a population, gripped by perceived oppression or political incompetence, collectively rises against its government.
While revolutions can take various forms, they invariably serve as a testament to the indomitable spirit of human agency and the enduring struggle for justice, liberty, and self-determination. This piece explores the multifaceted phenomenon of revolution, delving into its historical context, underlying causes, and far-reaching consequences.

Table of Contents
The Strength of Revolution
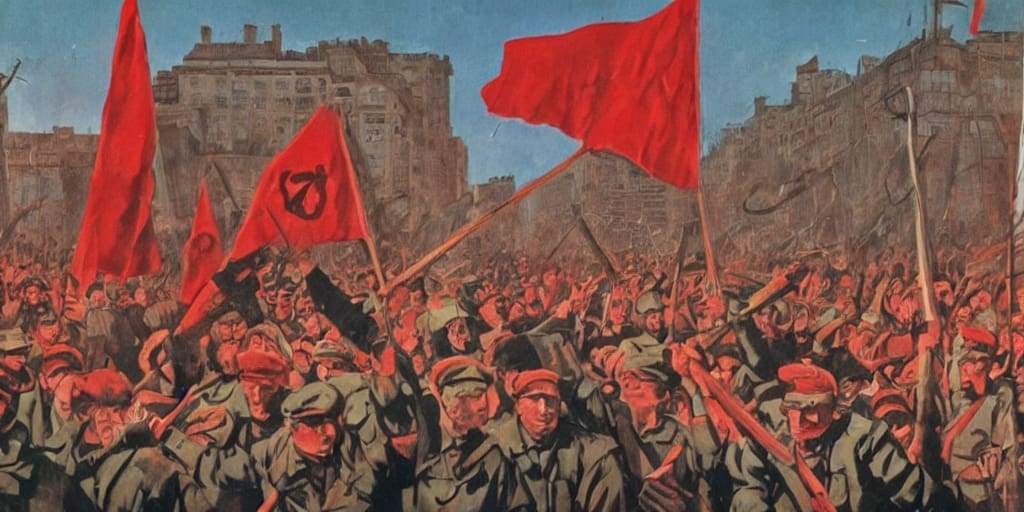
Revolutions have punctuated the historical narrative across centuries and continents. These tumultuous events, marked by significant political upheavals, have redefined the course of nations and left a lasting imprint on humanity. The French Revolution of 1789, the American Revolution of 1775, and the Bolshevik Revolution of 1917 are just a few examples of the transformative power of revolution.
The French Revolution, for instance, erupted as a response to a deeply entrenched system of monarchy and aristocracy, which had subjected the masses to political disenfranchisement and economic suffering. It resulted in the toppling of the Bourbon monarchy, the rise of revolutionary ideologies, and the eventual installation of the First French Republic.
Similarly, the American Revolution was a revolt against British colonial rule and its arbitrary impositions, ultimately leading to the establishment of the United States as an independent nation. The Bolshevik Revolution, on the other hand, was a product of profound social, political, and economic inequality in Tsarist Russia, culminating in the rise of communism and the Soviet Union.
*All Clothes Images are items from our shop souled-out.world
Causes of Revolution
Revolutions are complex phenomena driven by a convergence of factors that typically include political oppression, social injustice, economic disparities, and governmental incompetence. These underlying causes serve as the fertile ground upon which the seeds of revolution are sown.
Political Oppression: Perhaps the most common catalyst for revolution is the presence of oppressive political regimes. When governments consistently violate the rights and freedoms of their citizens, suppress dissent, and engage in authoritarian practices, the population is often pushed to its breaking point. It is the desperate cry for political liberty that frequently ignites the flames of revolution.
Social Injustice: Social inequality and discrimination can be a powerful fuel for revolution. When large segments of the population face discrimination, exploitation, or disenfranchisement, their collective anger can be harnessed to challenge the existing power structure. The demand for social justice becomes a rallying cry for revolutionary movements.
Economic Disparities: Economic grievances, especially extreme poverty and inequality, can galvanize people to rise against their rulers. When the majority of the population struggles to meet their basic needs while a tiny elite thrives, economic disparities can stoke the fires of revolution. Economic hardship often serves as a potent incentive for people to demand radical change.
Governmental Incompetence: Incompetent governance, characterized by mismanagement, corruption, and a lack of responsiveness to the needs of the populace, can erode public trust in the government. When the government’s inefficiency becomes a barrier to progress, citizens are more likely to rise against it in search of better leadership.
Consequences of Revolution
The consequences of revolution are profound and far-reaching, shaping the political landscape, societal norms, and even global dynamics. These transformative events not only redraw borders but also redefine the values and aspirations of societies.
Political Transformation: The primary outcome of a successful revolution is the overthrow of the existing regime and the establishment of a new political order. This can take various forms, from the establishment of democracies to the rise of authoritarian regimes, depending on the ideology and goals of the revolutionary forces.
Social and Cultural Change: Revolutions often trigger shifts in societal norms, values, and cultural practices. As societies evolve and become more inclusive and equitable, changes in gender roles, religious practices, and societal expectations may occur.
Economic Reconfiguration: Economic systems can be drastically altered after a revolution. Whether through nationalization, privatization, or the adoption of new economic ideologies, revolutionary governments often seek to address the economic disparities that contributed to the upheaval.
Global Impact: Revolutions are not isolated events. They can have significant global repercussions, influencing neighbouring countries, international relations, and the spread of ideological movements. The aftermath of revolutions can lead to regional instability or diplomatic realignments.
Lessons in Governance: Revolutions also serve as valuable lessons in governance. They highlight the importance of responsive and accountable leadership, protection of human rights, and social justice. The memory of past revolutions can influence the behaviour of governments and societies for generations.
Challenging the Status Quo
Revolution, as a fundamental and relatively sudden change in political power and organization, is a manifestation of the human spirit’s unwavering yearning for justice, liberty, and self-determination. Throughout history, oppressed and marginalized populations have risen against their rulers, reshaping the world in the process. Whether driven by political oppression, social injustice, economic disparities, or governmental incompetence, revolutions have demonstrated the capacity of human beings to challenge the status quo.
While the outcomes of revolutions are diverse, they undeniably leave a lasting impact on the societies they touch. Political transformations, changes in social and cultural norms, economic reconfigurations, and even global consequences all bear witness to the power of revolutionary movements. The study of revolution, as a phenomenon, serves as a reminder that the struggle for a more just and equitable world is a timeless pursuit and a testament to the resilience and adaptability of the human spirit.
More ‘Revolution’ Apparel in Our Souled-Out.World Shop

























Leave a Comment